Evaluate your self-service journey with concrete user stories

Almost every company offers digital self-services in addition to personal service.
However, user numbers are lagging well behind the desired development (digital gap).
Many companies have no transparency about the effectiveness of their digital services in relation to their customers.
Why is that the case?
Here are three main reasons for underutilization of digital service offerings and corresponding “closing the gap” approaches based on quantitative feedback from customer contacts:
Customers don´t want to use digital services or aren´t aware of them.
Customers use digital services, but fail with the solution.
A corresponding solution
for the specific customer request doesn´t exist.
Activate customers:
Specific activation of customers for use “next time” at all key touchpoints or interactions with the company.
Optimize the self-service journey: Structured learning from the experiences of customers who fail to use self-service and contact customer service.
Complete the solution set:
Relevant new use cases are implemented on the basis of a deep understanding of the requests that are suitable and desired for self-service.
Customers don´t want to use digital services or aren´t aware of them.
Activate customers:
Specific activation of customers for use “next time” at all key touchpoints or interactions with the company.
Customers use digital services, but fail with the solution.
Optimize the self-service journey: Structured learning from the experiences of customers who fail to use self-service and contact customer service.
A corresponding solution
for the specific customer request doesn´t exist.
Complete the solution set:
Relevant new use cases are implemented on the basis of a deep understanding of the requests that are suitable and desired for self-service.
That's why we have developed two efficient tools for you, that assess the status quo and provide you with concrete approaches for improvement:
Self-Service Survey
Quantitative study as part of a contact analysis
- Short contextual customer survey on the self-service experience during customer contact
- Weak point analysis and derivation of relevant use cases for optimization
Self-Service Assessment
Qualitative study with typical use cases/personas
- CX expert evaluation of the self-service journey based on selected and relevant use cases
- Concrete fields of action & potential for improving target achievement & UX quality (often with competitive comparison)
Self-Service Survey
Quantitative Studie im Rahmen einer Kontaktanalyse
- Short contextual customer survey on the self-service experience during customer contact
- Weak point analysis and derivation of relevant use cases for optimization
Self-Service Assessment
Qualitative Studie mit typischen Use Cases/Personas
- CX expert evaluation of the self-service journey based on selected and relevant use cases
- Concrete fields of action & potential for improving target achievement & UX quality (often with competitive comparison)
The main drivers for failure in self-service use are usability and customer effort in the following drivers:
They also form the evaluation criteria for our self-service assessment.
Accessibility
to the self-service offers
(e.g. portal registration, login)
Findability
of solutions in the digital service offerings
(e.g. search bar)
Comprehensibility
of the results and solutions
(e.g. FAQs not in customer language, complicated instructions)
Usability
of the solutions offered
(e.g. FAQs, instructions for solving issues in the portal)
Relevance
of the solutions offered
(e.g. no “perfect fit” solution to the request)
Next Issue Avoidance
to rule out potential follow-up issues
(e.g. proactively addressing typical follow-up activities after using the solution)
They also form the evaluation criteria for our self-service assessment.
Accessibility
to the self-service offers
(e.g. portal registration, login)
Findability
of solutions in the digital service offerings
(e.g. search bar)
Comprehensibility
of the results and solutions
(e.g. FAQs not in customer language, complicated instructions)
Usability
of the solutions offered
(e.g. FAQs, instructions for solving issues in the portal)
Relevance
of the solutions offered
(e.g. no “perfect fit” solution to the request)
Next Issue Avoidance
to rule out potential follow-up issues
(e.g. proactively addressing typical follow-up activities after using the solution)
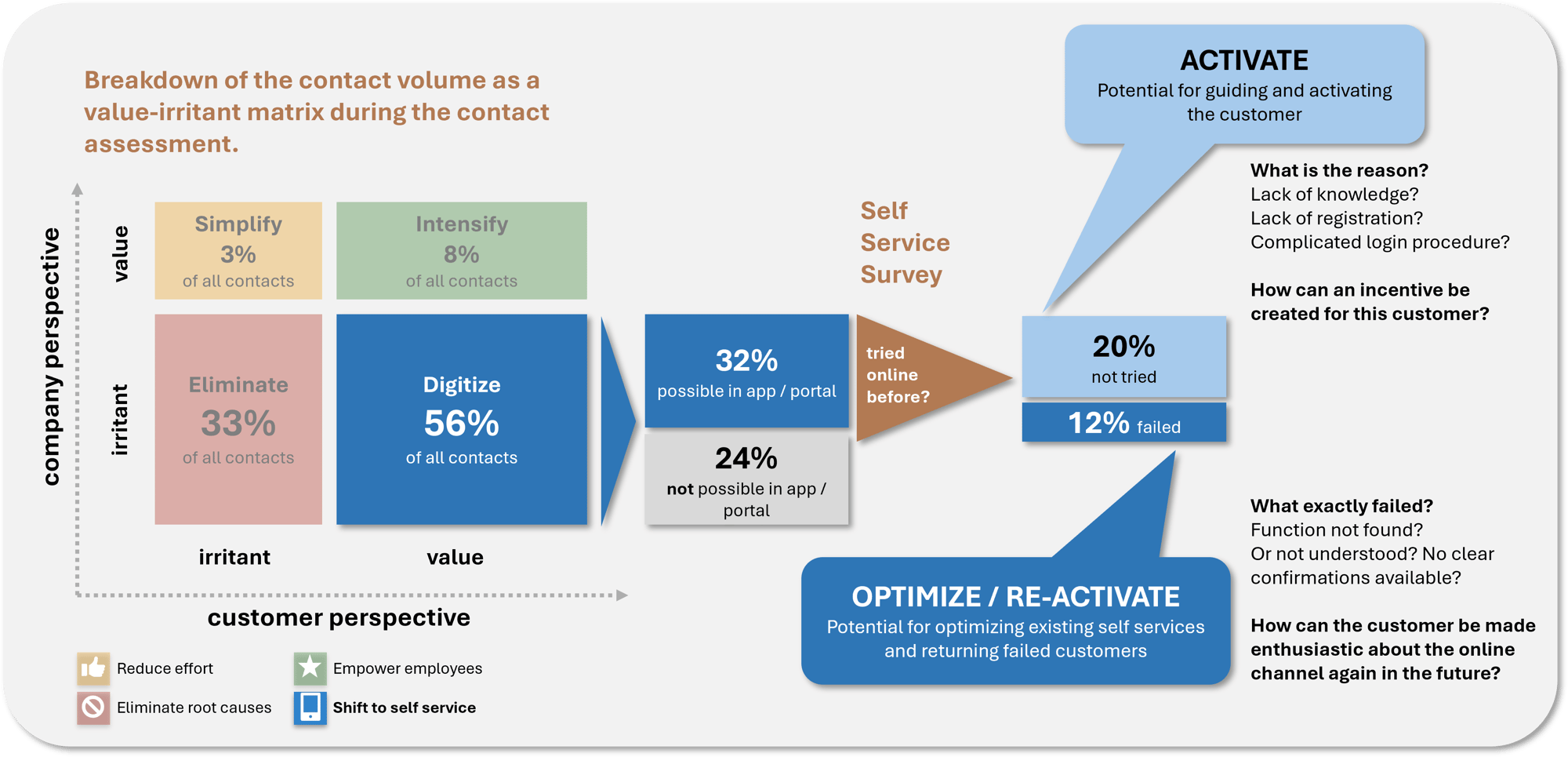
Here is an example of what the results and questions of a self-service survey can look like in a WOCAS® contact assessment:
Sounds good?
Did you find critical points while reading that sound familiar to you? Would you like to bring us on board as experts to offer your customers an optimal self-service journey? Then get in touch with us.
We look forward to hearing about your challenges and finding out together how WOCAS can help you.
